TWAIN was developed by a consortium of software and hardware manufacturers to standardize the communications between application programs and image acquisition devices. The interface is optimized for the acquisition of graphics images. The TWAIN standard is widely supported by scanner manufacturers. The most widely used version of TWAIN is v1.9 (as of this writing). In addition to scanners, TWAIN is being used with digital cameras and video capture boards. ImageGear supports all three TWAIN Transfer Modes: Native Data Transfer Mode (which is the TWAIN default), Disk File Transfer, and Buffered Memory.
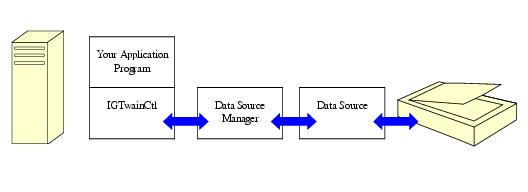
A TWAIN-compliant image acquisition device is one whose device driver complies with the TWAIN specification. The device driver understands the TWAIN protocol, thus allowing interaction with the Data Source Manager, the main interface module of the TWAIN software. The Data Source Manager "manages the session" between the application program and the raster-generating data source. Three software elements work together in TWAIN: the application, the Data Source (DS), and the Data Source Manager (DSM) as shown in the illustration below:
The following terminology is used to discuss ImageGear scanning:
The TWAIN Data Source for your device and the TWAIN Data Source Manager should be included as part of your scanner software. They are not part of the ImageGear software.
The process of acquiring an image (or set of images) from a device is as follows:
Thus, an example of the code needed to acquire an image from a TWAIN Data Source is as follows:
| C# |
Copy Code |
|---|---|
ImGearTWAIN igTWAIN = new ImGearTWAIN(); igTWAIN.WindowHandle = this.Handle; igTWAIN.UseUI = true; // Open a data source igTWAIN.OpenSource(""); // Set simplex mode ImGearCapOneValue igCapOneValue = new ImGearCapOneValue(ImGearCapabilities.CAP_DUPLEXENABLED); igCapOneValue.Value = false; igTWAIN.SetCapability(igCapOneValue, ImGearMessages.SET); // Acquire image ImGearPage igPage = igTWAIN.AcquireToPage(); // Close the data source igTWAIN.CloseSource(); | |